Knowledge
- Reference GPO templates
- Describe RDP requirements
- Locate ADM template files
- Explain GPO settings including Describe “build to lossless” and Describe how to configure cache size
- Identify maximum number of monitors and resolution
- Configure Flash quality and throttling
- Configure software 3D rendering capabilities
Reference GPO Templates
View comes with a number of built in Group Policy templates which are as follows:
For a full break down of each Group Policy setting, I recommend reading the VMware View Administration – View 5.0 guide.
Describe RDP Requirements
To enable users to connect to there View Desktop, RDP has to be enabled on the Operating System. When they grant the View Desktop Users access to a Restricted Group called ‘Remote Desktop Users’ and apply this group policy to the Organisational Unit that the View Desktops will be held.
I covered the configuration steps in VMware View – Objective 1.5 Preparing Active Directory For Installation under Section Remote Desktop Users.
The requirements for RDP are as follows:
- Remote Desktop Connection 6.x > Windows XP
- Remote Desktop Connection 6.x or 7.x > Windows Vista
- Remote Desktop Connnection 7.x > Windows 7
The good news any of the above RDC protocols support dual monitors!
Locate ADM Template Files
The ADM Template Files are located on your View Connection Server under …VMwareVMware ViewServerextrasGroupPolicyFiles
A bit like Blue Peter, I made this earlier which shows you how to import the ADM Templates VMware View – Objective 1.5 Preparing Active Directory For Installation under Template Files.
Explain GPO Settings Including Describe “Build To Lossless” and Describe How To Configure Cache Size
I feel like a parrot repeating myself, but here goes, for a full break down of each Group Policy setting, I recommend reading the VMware View Administration – View 5.0 guide.
One of the most important features of the PCoIP protocol is ‘build to lossless’ so what does this actually mean. Well the essence of ‘build to lossless’ is to give the user the best experience possible.
Let’s say a user is in a cafe, and the are using there mobile phone to act as there WAP. The likelihood is the connection will have high latency and there bandwidth is probably less than 1 Mbps. Rather than sending the complete desktop image immediately, the PCoIP protocol will send it in a ‘lossy’ state first which is a highly compressed initial image. As the connection continues more data is sent and the ‘lossy’ initial image becomes fully rendered.
The good news is the user, has no idea this is going on in the background, they just think it’s sheer awesomeness!
PCoIP is a clever little protocol, as it uses the clients (dumb terminal) memory to cache portions of the display to save them having to be re-transmitted and re-rendered. Currently this setting is only supported in Windows and Linux.
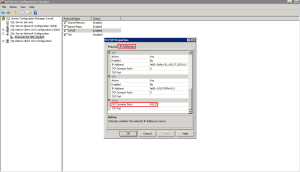
The VMware View PCoIP Session Variable ADM contains the setting. If this isn’t configured or enabled then PCoIP uses 250MB. If you do configure it, then the minimum setting is 50MB and the maximum is 300MB.
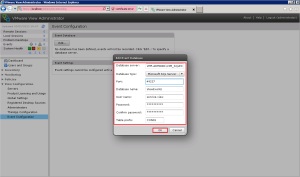
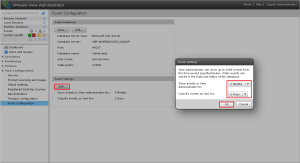
To get to this settings open up Group Policy Editor > View PCoIP > Computer Configuration > Policies > Administrative Templates > Classic Administrative Templates > PCoIP Session Variables > Not Overridable Administrator Settings > Configure PCoIP Client Image Cache Size Policy
Identify Maximum Number Of Monitors and Resolution
If you really want too, you can have four monitors running up to 2560 x 1600 display on each!
Or if you want to roll with 3D enabled, then I’m afraid it’s only two monitors at 1920 x 1200.
Configure Flash Quality and Throttling
Before we go into the configuration, a couple of items about Flash.
- Bandwidth reduction is only available in Internet Explorer with Flash version 9 or 10.
- Flash cannot be running in full screen mode
Flash settings are configured per pool. To change settings go too Inventory > Pools > Edit Pool Settings > Scroll Down to Adobe Flash Settings
Naturally, you can select the Flash settings that work best for your environment.
Configure Software 3D Rendering Capabilities
So you really want to use the Windows 7 Aero theme? Well good news is that View supports it, however you need to make sure the following requirements are met:
- ESXi 5.0 or later Hosts
- vCenter 5.0 or later
- Desktops must use Virtual Hardware 8 or later
- PCoIP must be used
- Users cannot choose there own display protocol
To enable 3D Rendering go too Inventory > Pools > Edit Pool Settings and change the following:
- Default display protocol PCoIP
- Allow users to choose protocol No
- Windows 7 3D Rendering Enabled